Gout
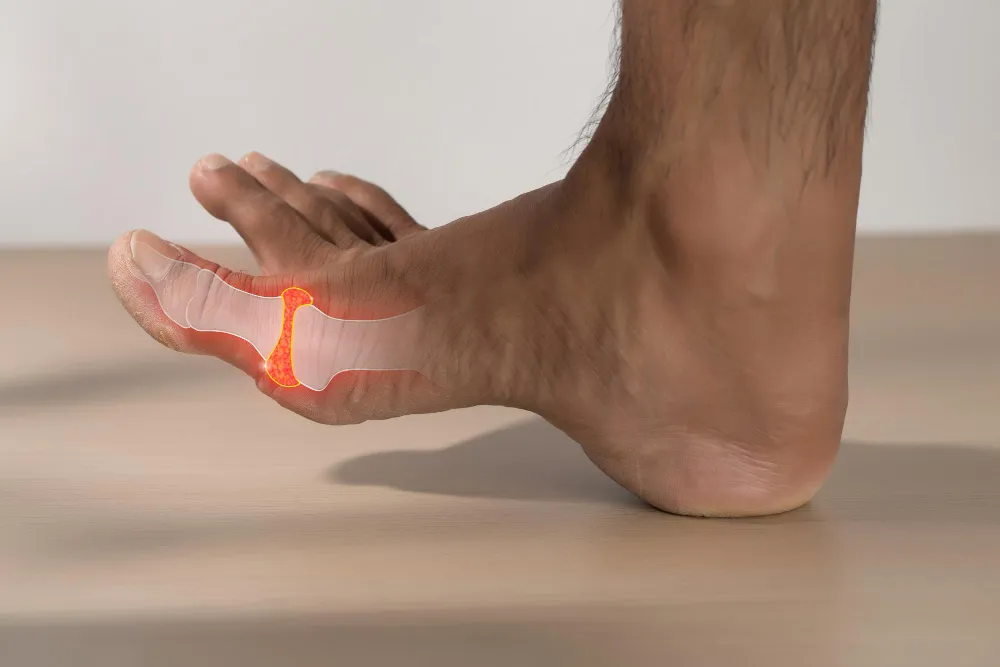
Understanding Gout
The “king of diseases and disease of kings” – but it can affect anyone.
What is Gout?
Gout is a common type of inflammatory arthritis caused by uric acid crystal deposits in the joints. It often presents with sudden, severe attacks of pain, redness, and swelling, most commonly in the big toe, but it can affect other joints too.
Who is at Risk?
- Men over 30 and postmenopausal women
- People with high uric acid levels (hyperuricemia)
- Those with obesity, high blood pressure, diabetes, or kidney disease
- Excessive alcohol consumption, especially beer and spirits
- High intake of purine-rich foods (red meat, organ meats, seafood)
Signs & Symptoms
- Sudden severe joint pain, often at night
- Redness, swelling, and warmth in the affected joint
- Commonly affects the big toe, but also knees, ankles, wrists, and elbows
- Attacks can last days to weeks if untreated
- Repeated episodes may lead to chronic gout with visible tophi (crystal lumps under the skin)
Why Early Diagnosis Matters
- Untreated gout can lead to chronic joint damage and deformity
- High uric acid is also linked to kidney stones and kidney disease
- With early treatment, flares can be controlled and prevented
Management & Lifestyle
RA is progressive, it worsens if left untreated.
- Medications:
- NSAIDs, colchicine, or steroids for acute attacks
- Uric acid-lowering drugs (allopurinol, febuxostat) for long-term prevention
- Diet & Lifestyle:
- Limit red meat, organ meats, shellfish, sugary drinks, and alcohol
- Stay hydrated
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Regular exercise
Takeaway Message
Gout is more than “just a painful toe.” It’s a metabolic and inflammatory disease that needs proper medical care.
Early treatment can prevent flares, protect joints, and keep life pain-free.
If you suffer from recurrent joint pain or swelling, check your uric acid and consult a rheumatologist.
